How can you run Xcode on Windows and develop iOS apps with a Windows PC? The short answer is: you can’t! You’ve got a few alternatives to get around that, however. In this tutorial, we’ll discuss how you can install Xcode on Windows to build iOS apps.
Here’s what we’ll get into:
- Rent a Mac in the cloud (starting at $20/mo)
- Run and compile Swift directly on Windows/Linux
- Learning to code with a Swift Sandbox
- Build your own “Hackintosh” by installing macOS on a PC
- Run Xcode on Windows by installing macOS on a virtual machine
- Develop iOS apps on Windows with cross-platform tools
- Get your hands on a second-hand Mac (starting at $300)
Let’s get to it!
Apr 04, 2018 Xamarin is a tool allowing you to build mobile apps for any platform with about 90% of shared code. This means you can create the same app for iOS and Android way faster and using a smaller team of developers than if you build native apps. Xamarin allows us to code in C just once and then deploy on the three platforms (Windows, iOS and Android), but without a Mac, the iOS environment might give us some problems. In Visual Studio, where Xamarin is installed, we have the Xamarin Mac Agent that allows you to run iOS Simulator.
Xcode for Windows: What & Why
Xamarin Build Ios App Without Mac
Xcode is the macOS-only software program, called an IDE, that you use to design, develop and publish iOS apps. The Xcode IDE includes Swift, a code editor, Interface Builder, a debugger, documentation, version control, tools to publish your app in the App Store, and much more.
Xcode contains everything you need to build iOS apps, and it only runs on macOS!
That’s when the problems start. You want to make an iOS app with your Windows PC, but you can’t buy a PC or laptop with macOS pre-installed on it. Unlike Windows, Apple doesn’t license its operating system to other computer manufacturers. You can only use macOS on a Mac.
In fact, when you obtain a license to use macOS, which happens when you purchase a Mac computer, you have to agree to only run the operating system on Apple hardware. This effectively limits you to only develop apps on a Mac.
“It’s more fun to be a pirate than to join the navy.”
— Steve Jobs (1983)
But… it’s more fun to be a pirate, than to join the navy, right? Let’s discuss a few alternatives that’ll let you run Xcode on Windows and develop iOS apps on a Windows PC!
Rent a Mac in the Cloud
An even easier way to get your hands on macOS, albeit more expensive, is to rent a Mac “in the Cloud”. You can work with Xcode on Windows with this approach, because you’re essentially connected to a Mac that’s elsewhere.
Here’s how that works:
- Someone connects a bunch of Mac’s to the internet
- You sign in on one of those Macs via a Remote Desktop Connection (RDP)
- Done! You can use this Mac from Windows/Linux and build iOS apps
Services like MacinCloud and MacStadium offer affordable rent-a-Mac products, usually paid on a monthly basis. Prices typically start at $20/month and you can choose from several hardware options, including Mac Mini and Mac Pro.
| Starting at | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| MacinCloud | $20/month | Dedicated, Virtual, Server |
| MacStadium | $79/month | Dedicated, Enterprise |
| virtualmacosx.com | $9.75/month | Shared (timesharing) |
| Mac Cloud | $49/month | Virtual |
| Flow | Premium | Dedicated, Enterprise |
| HostMyApple | $25/month | Virtual, Dedicated |
You connect to those cloud-based Macs via a Remote Desktop Connection (RDP). Windows includes a stock Remote Desktop Client you can use, and so do most Linux operating systems. Once you’re logged on, you can launch Xcode, and start building your iOS app. That way you’re effectively running Xcode on your Windows PC!

Cloud-based Macs usually come in 3 flavours:
Build Xamarin Ios Without Mac
- A dedicated Mac, which means you get access to a physical Mac located in a data center, as if you bought a Mac in the Apple Store and put it on your desk.
- A virtual Mac, which means you get access to a virtual Mac in a data center, much like the VirtualBox solution mentioned earlier. Your Mac won’t run on Apple hardware, but it will run macOS.
- A Mac Build Server, which is a specialized kind of Mac that can be used to compile iOS apps. You’ll create those apps on your Mac, and then instruct the Build Server to compile the app for you.
A dedicated Mac is the most convenient, and the most powerful option. A virtual Mac is OK too, but it typically does not perform as well as a physical Mac computer.
Running Xcode via a Mac in the cloud has a drawback: you can’t easily connect your iPhone to Xcode via USB! With Xcode on your local Mac you can run and debug your app on your own iPhone, via the USB/Lightning cable. This obviously won’t work when your Mac is in the cloud…
Don’t worry! There are plenty of solutions for that:
Xamarin Ios Tutorial
- A simple approach is to run your app on iPhone Simulator, right from within Xcode. You can launch iPhone Simulator in Xcode, and debug your app with it. This is perfect for the development phase of your project.
- An alternative solution are tools like Flexihub, NoMachine and USB Network Gate. They only work with dedicated Mac hardware, and you need to have a dedicated IP address.
- Install your iOS app on your iPhone via TestFlight, and debug it with a tool like Bugsnag. You can monitor and debug live crashes in your app.
An interesting use case for renting a Mac in the cloud comes from the latest developments in Apple’s hardware. Many designers, developers and desktop-publishers have voiced their concerns over Apple hardware lagging behind, offering low-spec computers for a fairly high price.
If you don’t want to take your $3.000 MacBook Pro with you in a coffee shop, or on your next trip to Thailand, why not purchase a low-end Windows or Linux laptop, and connect to your Mac in the cloud? You can either host it at home yourself, co-locate it in a data center, or rent a dedicated cloud-based Mac.
Do you want to learn how to code iOS apps, but don’t want to invest money in a Mac? Rent a Mac in the cloud for the duration of the iOS development course you’re taking! It’s a great way to bootstrap learning iOS development, and you can always buy your own Mac later.
Learn how to code iOS apps
Get started with Xcode and Swift
Ready to get started with iOS development? Learn how to code iOS apps with Xcode and Swift with our immersive iOS development course. Works both on Mac and PC!
Install macOS on Your Windows PC via VirtualBox
The easiest way to run Xcode on Windows is by using a virtual machine (VM).
A virtual machine will create an environment an operating system can run in, as if it’s running on the hardware itself, except it’s running “on top” of your actual hardware and operating system. You can then run Xcode normally, because it essentially runs on macOS on Windows!
This is called virtualization, and it allows you to run Windows on Linux, macOS on Windows, and even Windows on macOS. One of the benefits of virtualization is to run multiple OS side-by-side, which is useful for cross-platform development.
You need 2 things to run macOS on Windows in a VM:
- A copy of macOS, as an installer or virtual disk image file
- A virtual machine tool, like VirtualBox (free) or VMware (paid)
You can obtain a copy of macOS by downloading it from the App Store or by borrowing it from a friend. A great approach is to search for virtual disk images that have macOS pre-installed. You can also find installers from various sources on the internet, or upgrade a pre-existing image to a newer (beta) version of macOS.
Here’s what you do next:
- Install VirtualBox or VMware
- Mount the macOS installer or disk image
- Start the VM to launch macOS
- Launch Xcode!
You can read exactly how to in this tutorial. The recommended system specs are: 4-8 GB of RAM, an Intel i5/i7 compatible CPU, and at least 10 GB of free disk space.
Note: Using macOS on non-Apple hardware is against Apple’s End User License Agreement (EULA). (Fun fact: the same EULA prohibits the use of macOS to manufacture missiles or nuclear weapons…)
Build Your Own “Hackintosh” to Run Xcode
The most obvious choice to run Xcode on a Windows PC is perhaps to literally install macOS on a Windows PC…
“One platform to rule them all” has always been Apple’s take on the world. The Mac, App Store, iOS and Apple Music are all closed systems. Apple enthusiasts have always enjoyed the integrated Apple experience.
On the other hand, the rest of the world builds computers using an “open systems architecture”, in which you can effectively mix-and-match computer components and architectures to create your preferred computing machine.
Building $10.000 gaming PCs, mid-level desktops, blazing-fast ultrabooks, and $250 laptops is only possible because of open hardware. Because of Apple’s closed systems, you’re always bound by the hardware options they give you.
But… what if you want to run macOS on your custom built PC? Apple won’t let you, and your computer manufacturer can’t install macOS for you, even if they wanted to. Because macOS shall only run on Apple hardware!
Enter the “Hackintosh”.
A Hackintosh is a PC that runs macOS. Just like you can install macOS in a virtual machine, or in the cloud, you can install macOS as the bootable operating system on your PC. Switch it on, and macOS loads.
You can also create a dual-boot, i.e. a system that both hosts Windows and macOS. When you boot your PC, you can select the operating system that starts.
Building a Hackintosh can be a tricky exercise, especially if you’re not familiar with PC hardware and creating custom installations. Not all hardware is compatible with macOS. Moreover, Apple has of course created safe-guards against booting macOS on unsupported hardware.
Nevertheless, it’s a good option for running macOS on your custom hardware, and booting macOS on your Windows PC. Check out hackintosh.com for more information, and step-by-step guides.
The name “Hackintosh” comes from the old brand-name of Apple computers: Macintosh, combined with “hack”. Again, it’s against Apple’s EULA – but you wanted to be a pirate, right?
The days of the Hackintosh are almost over, depending on who you ask. Apple’s newer hardware includes a T2 chip now. Hardware-specific chips are notoriously hard to mimic in non-Apple hardware, which essentially means that, in the future, you may not be able to install or update macOS on a computer that doesn’t have that T2 chip.
Swift for Windows & Linux
Developers who want to learn Swift have 2 alternative approaches to code Swift, next to working with Xcode on Windows. Swift is open source, which means you can essentially run it on any system.
Currently, you can use:
- Swift 5 on Ubuntu Linux 16.04 and 18.04 via the official images
- Swift 4.1 on Windows 10 via the unofficial swiftforwindows.github.io
Here’s how you can run Swift code on Linux:
- Download the latest release from swift.org/download
- Unzip the
.zipin a convenient location - Locate the
swiftexecutable in theusr/bindirectory - Compile and run a Swift file with
swift [filename.swift]
You can also copy the Swift executables to your $PATH, or add Swift’s folder to $PATH, to use the swift command anywhere on your system.
Here’s how you can run Swift code on Windows:
- Download the latest release of Swift for Windows from this page
- Start the program and point it to your
.swiftfile - Click Run in the program
It appears the Swift for Windows project hasn’t been updated in a while. It’s latest supported version is Swift 4.1., which doesn’t differ that much from Swift 5 in terms of beginner syntax and functionality. Your mileage may vary, though!
You can even run and compile Swift on the $35 Raspberry Pi single-board computer! You can download Swift 5, which has been ported to the ARM CPU architecture, right here. Installing is as easy as pointing your RPi to the swift-arm repo, then do sudo apt-get install swift5, and then run the Swift CLI with swift [filename.swift]. Neat!
Develop iOS Apps on Windows With Cross-Platform Tools
Cross-platform tools are awesome: you code your app once, and export it to iOS and Android. That could potentially cut your app development time and cost in half. Several cross-platform tools allow you to develop iOS apps on a Windows PC, or allow you to compile the app if there’s a Mac in your local network.
Well, not so fast…
The cross-platform tool ecosystem is very large. On the one side you have complete Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like Xamarin, that allow you to build cross-platform apps with C#.
The middle ground is covered by tools like PhoneGap, Cordova, Ionic and Appcelerator, that let you build native apps with HTML5 components. The far end includes smaller platforms like React Native that allow you to write native apps with a JavaScript wrapper.
The one thing that stands out for all cross-platform tools is this: they’re not beginner friendly! It’s much easier to get access to a Mac, learn Swift, and build a simple app, than it is to get started with Xamarin.
Most of the cross-platform tools require you to have a basic understanding of programming, compilation options, and the iOS and Android ecosystems. That’s something you don’t really have as a beginner developer!
Having said that, let’s look at a couple of options:
- If you’re familiar with Windows-based development tools and IDEs, and if you already know how to code, it’s worthwhile to check out Xamarin. With Xamarin you code apps in C#, for multiple platforms, using the Mono and MonoTouch frameworks.
- If you’re familiar with web-based development, check out PhoneGap or Ionic. You’ll feel right at home with HTML 5, CSS and JavaScript. Don’t forget: a native app works different than a website…
- If you’re familiar with JavaScript, or if you’d rather learn to code JavaScript than Swift, check out React Native. With React Native you can code native apps for iOS and Android using a “wrapper”.
Choose deliberately for a cross-platform tool because it fits your project, not because you think a native platform language is bad. The fact that one option isn’t right, doesn’t immediately make another option better!
If you don’t want to join the proprietary closed Apple universe, don’t forget that many cross-platform tools are operated by equally monopolistic companies like Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Adobe and Amazon.
An often heard argument against cross-platform tools is that they offer limited access to and support for smartphone hardware, and are less “snappy” than their native counterparts. Also, any cross-platform tool will require you to write platform-specific code at one point, especially if you want to code custom features.
Note: You’ll still need to compile your app with Xcode, even if you use cross-platform tools. Most cross-platform tools rely on the command-line tools that are shipped with Xcode, as part of macOS. You’ll also need Xcode to publish your app in the App Store.
Get a Second-Hand Mac
You gotta ask yourself: Why not get a Mac? Perhaps the simplest option to build iOS apps with Xcode, in this tutorial, is purchasing a Mac for iOS development.
If you don’t want to tinker with cross-platform tools, or rent-a-Mac in the cloud, and just want to get started with iOS development: get a Mac.
A simple search on Ebay shows you 1-3 year old second-hand Mac Mini’s for as little as $250. Any newer, decent second-hand Mac Mini will set you back around $450. Don’t forget that you can get a brand new Mac Mini for around $800.
A better question is perhaps: is a Mac Mini from 2015 fast enough to build apps with? I’ve built 50+ apps for iOS, Android and the web since 2009, and a fair share of those were built on a 1.2 Ghz 8GB MacBook Air from 2013. I started LearnAppMaking.com with that same trusty ol’ MacBook, and I’ve coded several successful production apps with it until 2018.
It’s traveled with me all over the world, from the beaches of Thailand, to airline lounges, to coffee shops, to coding apps with my knees behind my ears, cramped in economy class at 20.000 feet up in the air.
I don’t want to go all nostalgic on you, but I learned to code on a 100 Mhz i486 PC, when lines still started with a number. That’s a lot faster PC than the one that put man on the moon, at 46 Khz.
So, to say that a Mac Mini, or your new 2015 MacBook Pro, is fast enough, is an understatement…
If you buy a second hand Mac, make sure that it supports the latest version of macOS. Xcode and iOS versions are connected to macOS versions, so you want to buy a Mac that supports at least the current ones. You can find the max. latest version of Xcode that your Mac can run, by cross-referencing the min macOS to run in this wiki with Hardware compatibility in this wiki.
Code Swift with a Swift Sandbox
Do you really need Xcode to code apps? Ultimately, yes. But you can definitely learn Swift and code Swift without a Mac or Xcode!
Here, check this out:
if i <= 2 {
return 1
} else {
return fibonacci(i - 1) + fibonacci(i - 2)
}
}
let numbers = Array(1...10).map { fibonacci($0) }
print(numbers)
The above code runs in a Swift sandbox. The sandbox sends the Swift code to a webserver, which compiles it and returns the result. It’s the perfect tool to quickly play with some Swift code in your browser!
Swift is an open-source language, and that means you can effectively run it on any hardware.
Need more space for your Swift code? Check out the bigger Swift Sandbox right here!
Learn how to code iOS apps
Get started with Xcode and Swift
Ready to get started with iOS development? Learn how to code iOS apps with Xcode and Swift with our immersive iOS development course. Works both on Mac and PC!
Further Reading
You can’t build iOS apps without Xcode, and you need macOS to run Xcode, and a Mac to use macOS. There’s no getting around it, except for these alternatives to run Xcode on Windows:
- Rent a Mac in the cloud (starting at $20/mo)
- Run Xcode on Windows by installing macOS on a virtual machine
- Build your own “Hackintosh” by installing macOS on a PC
- Develop iOS apps on Windows with cross-platform tools
- Get your hands on a second-hand Mac (starting at $300)
- Learning to code with a Swift Sandbox
- Run and compile Swift directly on Windows/Linux
Awesome. I want to wish you best of luck with building your iOS app on Windows! Here are a few projects and tutorials to consider:
-->This guide describes how to use Pair to Mac to connect Visual Studio 2019to a Mac build host. The same instructions apply to Visual Studio 2017.
Overview
Building native iOS applications requires access to Apple's build tools,which only run on a Mac. Because of this, Visual Studio 2019 must connect toa network-accessible Mac to build Xamarin.iOS applications.
Visual Studio 2019's Pair to Mac feature discovers, connects to,authenticates with, and remembers Mac build hosts so that Windows-basediOS developers can work productively.
Pair to Mac enables the following development workflow:
Developers can write Xamarin.iOS code in Visual Studio 2019.
Visual Studio 2019 opens a network connection to a Mac build host anduses the build tools on that machine to compile and sign the iOS app.
There is no need to run a separate application on the Mac – VisualStudio 2019 invokes Mac builds securely over SSH.
Visual Studio 2019 is notified of changes as soon as they happen. Forexample, when an iOS device is plugged in to the Mac or becomes availableon the network, the iOS Toolbar updates instantly.
Multiple instances of Visual Studio 2019 can connect to the Macsimultaneously.
It's possible to use the Windows command-line to build iOS applications.
Note
Before following the instructions in this guide, complete the following steps:
- On a Windows machine, install Visual Studio 2019
- On a Mac, install Xcode and Visual Studio for Mac
- You must manually open Xcode after installing so that it can add any additional components.
If you would prefer not to install Visual Studio for Mac, Visual Studio 2019can automatically configure the Mac build host with Xamarin.iOS and Mono.You must still install and run Xcode.For more information, see Automatic Mac provisioning.
Enable remote login on the Mac
To set up the Mac build host, first enable remote login:
On the Mac, open System Preferences and go to the Sharing pane.
Check Remote Login in the Service list.
Make sure that it is configured to allow access for All users, orthat your Mac username or group is included in the list of allowedusers.
If prompted, configure the macOS firewall.
If you have set the macOS firewall to block incoming connections, youmay need to allow
mono-sgento receive incoming connections. An alertappears to prompt you if this is the case.If it is on the same network as the Windows machine, the Mac shouldnow be discoverable by Visual Studio 2019. If the Mac is still notdiscoverable, try manually adding a Mac or takea look at the troubleshooting guide.
Connect to the Mac from Visual Studio 2019
Now that remote login is enabled, connect Visual Studio 2019 to the Mac.
In Visual Studio 2019, open an existing iOS project or create a new oneby choosing File > New > Project and then selecting an iOS projecttemplate.
Open the Pair to Mac dialog.
Use the Pair to Mac button iOS toolbar:
Or, select Tools > iOS > Pair to Mac.
The Pair to Mac dialog displays a list of all previously-connectedand currently-available Mac build hosts:
Select a Mac in the list. Click Connect.
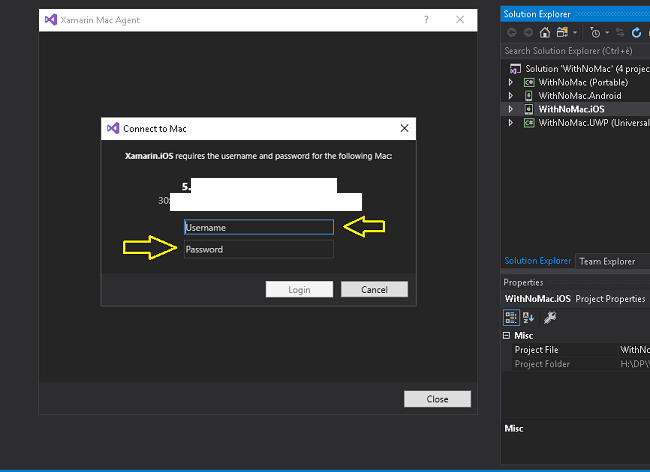
Enter your username and password.
The first time you connect to any particular Mac, you areprompted to enter your username and password for that machine:
Tip
When logging in, use your system username rather than full name.
Pair to Mac uses these credentials to create a new SSH connectionto the Mac. If it succeeds, a key is added to the authorized_keysfile on the Mac. Subsequent connections to the same Mac will loginautomatically.
Pair to Mac automatically configures the Mac.
Starting with Visual Studio 2019 version15.6,Visual Studio 2019 installs or updates Mono and Xamarin.iOS on aconnected Mac build host as needed (note that Xcode must still beinstalled manually). See Automatic Macprovisioning for more details.
Look for the connection status icon.
When Visual Studio 2019 is connected to a Mac, that Mac's itemin the Pair to Mac dialog displays an icon indicating thatit is currently connected:
There can be only one connected Mac at a time.
Tip
Right-clicking any Mac in the Pair to Mac list brings up a contextmenu that allows you to Connect..., Forget this Mac, orDisconnect:
If you choose Forget this Mac, your credentials for the selectedMac will be forgotten. To reconnect to that Mac, you will need to re-enteryour username and password.
If you have successfully paired to a Mac build host, you are ready to buildXamarin.iOS apps in Visual Studio 2019. Take a look at theIntroduction to Xamarin.iOS for Visual Studioguide.
If you have not been able to pair a Mac, try manually adding aMac or take a look at the troubleshootingguide.
Manually add a Mac
If you do not see a particular Mac listed in the Pair to Mac dialog,add it manually:
Locate your Mac’s IP address.
Open System Preferences > Sharing > Remote Login on your Mac:
Alternatively, use the command line. In Terminal, issue this command:
Depending on your network configuration, you may need to use aninterface name other than
en0. For example:en1,en2, etc.
In Visual Studio 2019's Pair to Mac dialog, select Add Mac...:
Enter the Mac's IP address and click Add:
Enter your username and password for the Mac:
Tip
When logging in, use your system username rather than full name.
Click Login to connect Visual Studio 2019 to the Mac over SSH and addit to the list of known machines.
Automatic Mac provisioning
Starting with Visual Studio 2019 version 15.6,Pair to Mac automatically provisions a Mac with software necessary forbuilding Xamarin.iOS applications: Mono, Xamarin.iOS (the softwareframework, not the Visual Studio for Mac IDE), and various Xcode-relatedtools (but not Xcode itself).
Important
- Pair to Mac cannot install Xcode; you must manually install it on theMac build host. It is required for Xamarin.iOS development.
- Automatic Mac provisioning requires that remote login isenabled on the Mac, and the Mac must be network-accessible to the Windowsmachine. See Enabling remote login on the Macfor more details.
- Automatic Mac provisioning requires 3GB of free space on the Mac to install Xamarin.iOS.
Pair to Mac performs necessary software installations/updates when VisualStudio 2019 is connecting to theMac.
Mono
Pair to Mac will check to make sure that Mono is installed. If it is notinstalled, Pair to Mac will download and install the latest stable versionof Mono on the Mac.
Progress is indicated by various prompts, as shown by the followingscreenshots (click to zoom):
| Install Check | Downloading | Installing |
|---|---|---|
| Mono |
Xamarin.iOS
Pair to Mac upgrades Xamarin.iOS on the Mac to match the versioninstalled on the Windows machine.
Important
Pair to Mac will not downgrade Xamarin.iOS on the Mac from alpha/betato stable. If you have Visual Studio for Mac installed, set yourrelease channel asfollows:
- If you use Visual Studio 2019, select the Stable updates channel inVisual Studio for Mac.
- If you use Visual Studio 2019 Preview, select the Alpha updateschannel in Visual Studio for Mac.
Progress is indicated by various prompts, as shown by the followingscreenshots (click to zoom):
| Install Check | Downloading | Installing |
|---|---|---|
| Xamarin.iOS |
Xcode tools and license
Pair to Mac will also check to determine whether Xcode has been installedand its license accepted. While Pair to Mac does not install Xcode, itdoes prompt for license acceptance, as shown in the following screenshots(click to zoom):
| Install Check | License Acceptance |
|---|---|
| Xcode |
Additionally, Pair to Mac will install or update various packagesdistributed with Xcode. For example:
Run Xamarin App On Ios Device Without Mac
- MobileDeviceDevelopment.pkg
- XcodeExtensionSupport.pkg
- MobileDevice.pkg
- XcodeSystemResources.pkg
The installation of these packages happens quickly and without a prompt.
Note
These tools are distinct from the Xcode Command Line Tools, whichas of macOS 10.9 areinstalled with Xcode.
Troubleshooting automatic Mac provisioning
If you encounter any trouble using automatic Mac provisioning, take a lookat the Visual Studio 2019 IDE logs, stored in%LOCALAPPDATA%XamarinLogs16.0. These logs may contain error messagesto help you better diagnose the failure or get support.
Build iOS apps from the Windows command-line
Pair to Mac supports building Xamarin.iOS applications from the commandline. For example:
The parameters passed to msbuild in the above example are:
ServerAddress– The IP address of the Mac build host.ServerUser– The username to use when logging in to the Mac build host.Use your system username rather than your full name.ServerPassword– The password to use when logging in to the Mac build host.
Note
Visual Studio 2019 stores msbuild in the following directory:C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft Visual Studio2019<Version>MSBuildCurrentBin
The first time Pair to Mac logs in to a particular Mac build host fromeither Visual Studio 2019 or the command-line, it sets up SSH keys. With thesekeys, future logins will not require a username or password. Newlycreated keys are stored in %LOCALAPPDATA%XamarinMonoTouch.
If the ServerPassword parameter is omitted from a command-line buildinvocation, Pair to Mac attempts to log in to the Mac build hostusing the saved SSH keys.
Summary
This article described how to use Pair to Mac to connect Visual Studio 2019 to aMac build host, enabling Visual Studio 2019 developers to build native iOSapplications with Xamarin.iOS.